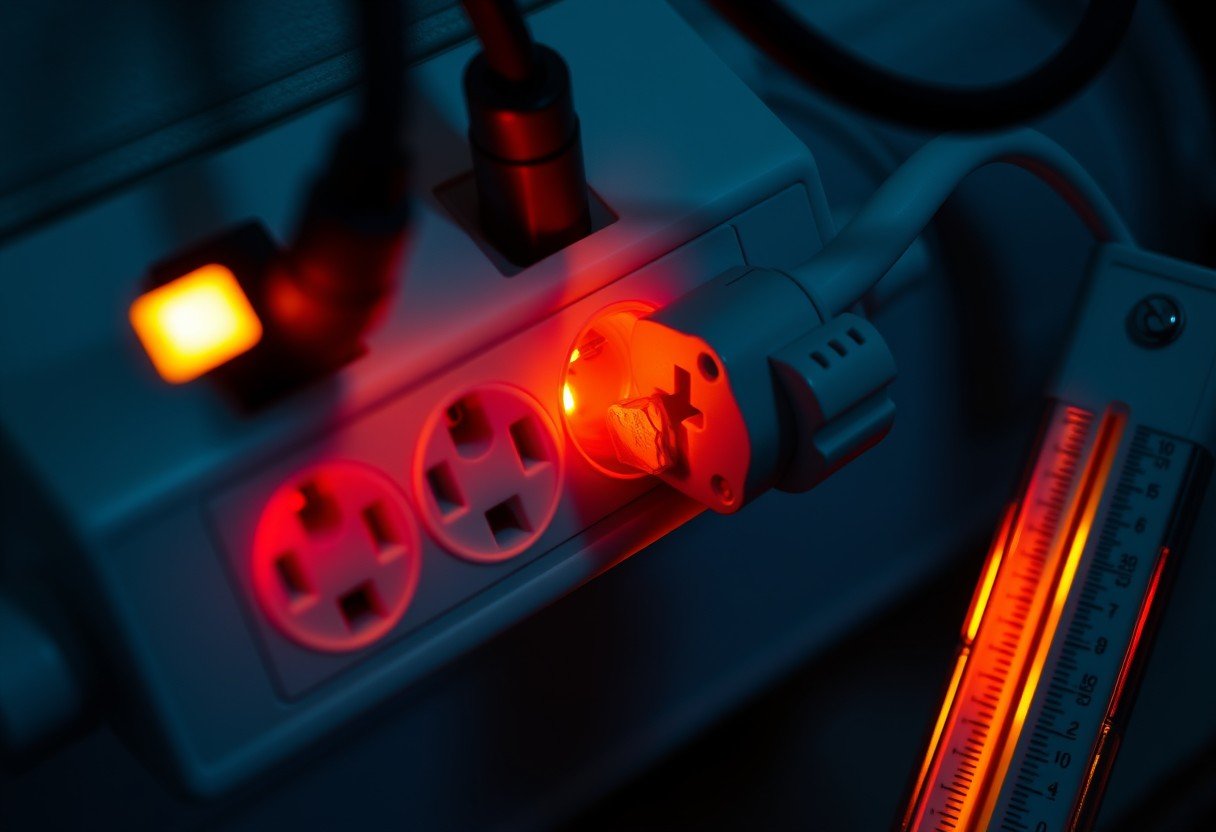
It’s normal to feel a power strip get slightly warm, but when it becomes hot to the touch, it’s a warning sign. This heat is often caused by electrical resistance, overloading from too many devices, or poor ventilation. Understanding these causes is the first step to preventing potential dangers like electrical fires and protecting your valuable electronics. Ignoring a hot power strip can lead to serious safety hazards in your home or office.
What Causes a Power Strip to Overheat?
Several factors can turn a convenient power strip into a potential hazard. The most common reasons involve putting too much electrical demand on the device, which it isn’t designed to handle. This excessive load is a primary cause of dangerous heat buildup.
When you plug too many devices into one strip, especially high-power appliances, you risk exceeding its maximum wattage capacity. Every power strip has a limit, and pushing past it forces the internal components to work too hard, generating significant heat. According to the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission, overloaded electrical circuits are a leading cause of residential fires.
Faulty or aging wiring also plays a big role. Over time, the internal connections can loosen, or the wires can degrade. This creates higher electrical resistance, which translates directly into heat whenever electricity flows through. A poorly made power strip with thin wiring is much more likely to overheat even under a normal load.
The Importance of Proper Ventilation
You might not think of a power strip as a device that needs to “breathe,” but proper airflow is crucial for its safety. When a power strip is running, it naturally generates some heat. Without a way for that heat to escape, the temperature can quickly rise to dangerous levels.
Placing a power strip in a confined space is a common mistake. Locations to avoid include:
- Underneath a thick carpet or rug
- Behind bulky furniture pressed against a wall
- Inside a closed cabinet or drawer
These environments trap heat, creating an insulating effect that can cause the strip’s plastic casing to melt and potentially start a fire. Furthermore, dust and debris can accumulate in and around the power strip, blocking ventilation holes and acting as another layer of insulation. Keeping the area around your power strip clean and open is a simple but effective safety measure.
How Quality and Age Affect Safety
Not all power strips are built the same. The quality of materials and construction directly impacts how well a strip manages heat and how safe it is over its lifespan. Cheaper power strips often use thinner gauge wiring and lower-quality plastic that cannot withstand heat as effectively.
An older power strip is also more susceptible to overheating. Constant use causes wear and tear on internal components like the wiring, plugs, and circuit breaker. This degradation increases electrical resistance, leading to more heat. Always choose power strips with safety certifications from recognized organizations like UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or CSA (Canadian Standards Association). This label means the product has been rigorously tested to meet strict safety standards.
When choosing a new power strip, consider these key factors to ensure you are getting a safe and reliable device.
| Consideration | Importance |
| Power Rating | Ensures it can handle the combined wattage of all devices. |
| Surge Protection | Protects against electrical surges and damage. |
| Number of Outlets | Determines how many devices you can connect effectively. |
| Safety Features | Includes circuit breakers, over-current protection, etc. |
Warning Signs of a Failing Power Strip
A power strip will often give you clear signals that it is overheating or failing. Recognizing these signs early can prevent damage to your devices and avert a potential fire. You should immediately stop using a power strip if you notice any of these issues.
Pay close attention to any physical changes or unusual smells. If the plastic casing feels very hot to the touch, not just warm, it is a major red flag. Other critical signs include discoloration or scorch marks around the outlets, which indicate intense heat. A persistent burning smell is one of the most serious warnings and means you should unplug the strip from the wall immediately.
Simple Steps for Safe Power Strip Use
Following a few best practices can dramatically reduce the risk of your power strip overheating. Proper usage is just as important as buying a quality product. Making these habits part of your routine will help ensure your home and electronics stay safe.
The most important rule is to never plug high-power appliances into a power strip. Devices like refrigerators, space heaters, microwaves, and coffee makers draw a large amount of current and should always be plugged directly into a wall outlet.
Here are some essential safety practices to follow:
- Check the Wattage: Before plugging anything in, know the power strip’s maximum capacity and the total wattage of the devices you want to connect.
- Avoid Daisy-Chaining: Never plug one power strip into another. This creates a severe overload risk and is a common cause of electrical fires.
- Inspect Regularly: Check your power strips periodically for any signs of damage, such as frayed cords, cracked casing, or loose plugs.
- Unplug When Not in Use: Unplugging devices that aren’t being used reduces the electrical load and saves energy.
By being mindful of how you use your power strips, you can easily avoid the common pitfalls that lead to overheating.
Frequently Asked Questions about Power Strip Safety
Why does my power strip get warm even with nothing plugged in?
A power strip should not feel warm if nothing is plugged into it. Some models with features like indicator lights or USB ports may feel slightly warm, but if a basic strip is warm while empty, it could have an internal fault and should be replaced.
Is it okay to use a power strip that is hot to the touch?
No, you should never continue to use a power strip that is hot. Immediately unplug it from the wall, disconnect all devices, and allow it to cool. Once cool, inspect it for damage. If you find any issues or are unsure, it is safest to discard and replace it.
What is the difference between a power strip and a surge protector?
A basic power strip is simply an extension cord with extra outlets. A surge protector looks similar but includes electronic components that protect your connected devices from sudden voltage spikes, which can damage sensitive electronics.
How often should I replace my power strips?
There is no strict expiration date, but it is a good idea to inspect your power strips annually. Consider replacing them every few years, especially if they are used heavily or show any signs of wear like discoloration, cracks, or a loose-fitting plug.
Can I plug a space heater or an air conditioner into a power strip?
No, you should never plug high-demand appliances like space heaters, air conditioners, or refrigerators into a power strip. These devices draw too much power and can easily overload the strip, creating a serious fire hazard. They must be plugged directly into a wall outlet.








Leave a Comment