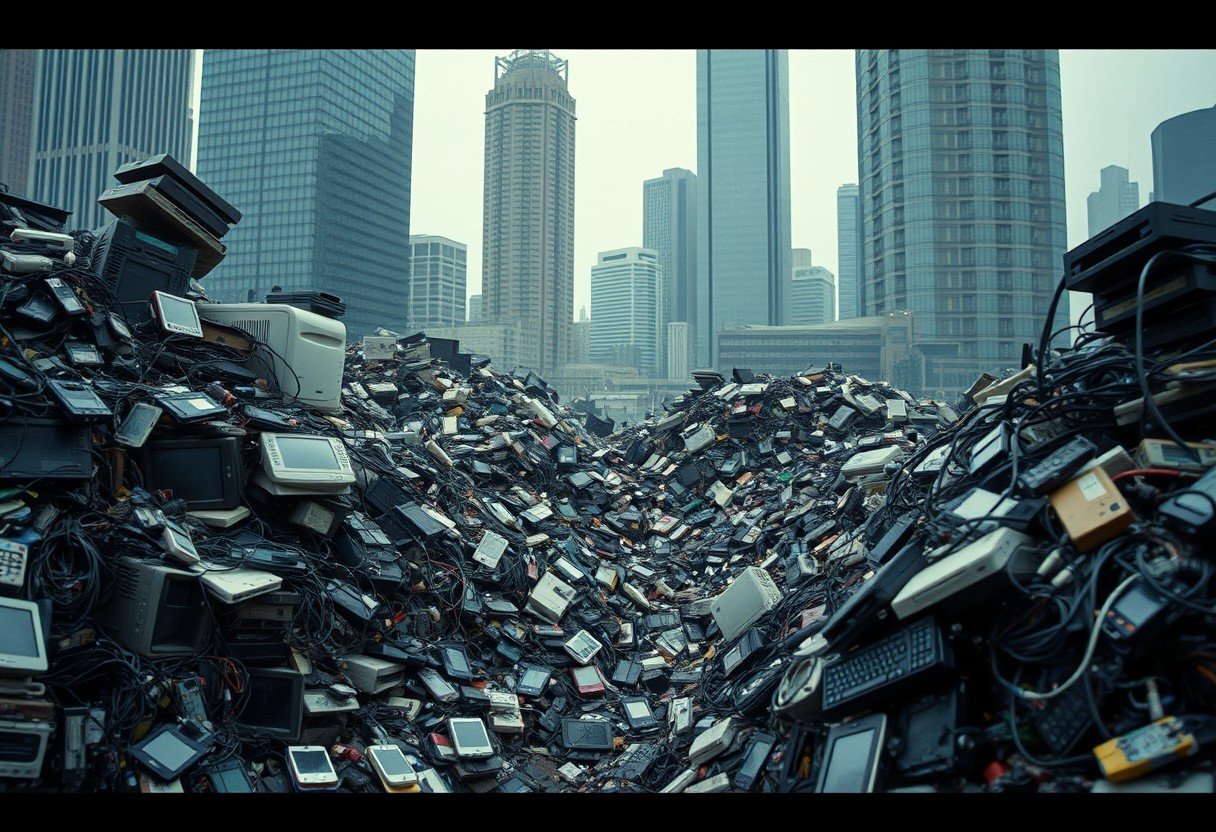
E-waste, or discarded electronic devices, has become a massive global issue in the 21st century. As technology advances faster than ever, we replace our gadgets more frequently, creating mountains of electronic junk. This surge in e-waste poses serious threats to our environment and health because old electronics contain harmful materials. Understanding this problem is the first step toward finding a solution.
What Exactly Qualifies as E-waste?
E-waste is a simple term for any electrical or electronic device that has been discarded. This includes a huge range of products that are no longer wanted, have stopped working, or are considered obsolete.
You might be surprised by what counts as e-waste. It’s not just big items like broken refrigerators or old desktop computers. Everyday items like smartphones, tablets, televisions, and even kitchen appliances contribute to the problem.
Even the smallest electronics, such as chargers, cables, and batteries, become e-waste when you throw them away. Because technology is always changing, we are constantly upgrading our devices, which creates a steady stream of old electronics that need to be disposed of properly.
The Main Drivers Behind the E-waste Surge
The rapid growth of e-waste in the 21st century is not an accident. It is driven by a combination of technological progress and our own buying habits. As new gadgets with exciting features are released each year, older models quickly become outdated.
This cycle of constant innovation leads to shorter product lifespans. A phone that was top-of-the-line two years ago might seem slow and obsolete today. This encourages a “throwaway culture” where we replace functional devices just to have the latest model.
Our consumption patterns have changed dramatically. The desire for new technology fuels a cycle of buying and discarding. Making conscious choices, like repairing a device instead of replacing it, can make a huge difference. Your habits matter, and changing them can help create a more sustainable future.
The Hidden Dangers to Our Environment
When you throw away an old electronic device, it doesn’t just disappear. Improper disposal of e-waste causes significant harm to our environment. Many electronics contain hazardous materials that can poison our natural world.
These toxic substances can seep into the ground when left in landfills, contaminating soil and groundwater. This pollution can harm plants, animals, and entire ecosystems for many years.
Some of the most dangerous chemicals found in e-waste include:
- Lead: Found in old TV screens and computer monitors, it can cause severe damage to the nervous system.
- Mercury: Used in some flat-screen displays and batteries, it is highly toxic to humans and wildlife.
- Cadmium: Often found in rechargeable batteries, it can cause kidney damage and is a known carcinogen.
The pollution from these materials disrupts the delicate balance of nature. It can lead to a loss of biodiversity, affecting everything from small insects to large mammals and threatening the overall health of our planet.
How E-waste Puts Human Health at Risk
The dangers of e-waste are not limited to the environment; they also pose a direct threat to human health. Exposure to the toxic components inside electronics can lead to a wide range of serious health problems.
When e-waste is burned or dismantled improperly, it releases harmful toxins into the air and water. People living near informal recycling sites can suffer from neurological damage, respiratory issues, and an increased risk of cancer.
Vulnerable communities, especially those in developing countries where much of the world’s e-waste is shipped, face the greatest risks. Workers, including children, often handle these hazardous materials without proper safety equipment. This ongoing exposure can cause long-term, debilitating health conditions, making it a critical human rights issue.
Global Efforts to Manage the E-waste Crisis
Recognizing the growing threat, nations around the world are starting to take action. International agreements and local initiatives are being developed to manage e-waste more responsibly.
Major international treaties, like the Basel Convention, aim to control the movement of hazardous waste between countries. In Europe, the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive makes manufacturers responsible for collecting and recycling their products. These frameworks are designed to hold companies accountable and promote sustainability on a global scale.
At the local level, community efforts are making a big impact. Many cities now host e-waste collection events, making it easier for you to drop off old devices safely. These programs not only ensure proper recycling but also raise awareness about why responsible disposal is so important for protecting our communities.
Simple Steps You Can Take for Responsible Disposal
Solving the e-waste crisis starts with the choices you make as a consumer. By adopting more responsible habits, you can play a crucial role in reducing waste and protecting the environment.
Instead of throwing out old electronics, look for ways to extend their life. Repairing a broken device or donating a functional one can keep it out of the landfill. When a device truly reaches its end of life, make sure to find a certified e-waste recycler.
Your actions can create a ripple effect. By sharing information with friends and family, you help build a community that values sustainable practices. Here is a simple guide to help you manage your old electronics:
| Do This | Don’t Do This |
|---|---|
| Repair your devices when possible. | Throw electronics in the regular trash. |
| Donate or sell working electronics. | Leave old gadgets in a drawer to collect dust. |
| Find a certified e-waste recycler. | Put batteries or light bulbs in the recycling bin. |
| Buy products from eco-conscious brands. | Upgrade your devices every single year. |
Being a mindful consumer is one of the most powerful ways to combat the e-waste problem. Every device you repair or recycle contributes to a healthier planet for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions about E-waste
What are the most common sources of e-waste in households?
The most common sources include large appliances like refrigerators and washing machines, IT equipment like laptops and smartphones, and entertainment devices like televisions and gaming consoles. Even small items like chargers and electric toothbrushes contribute.
Why can’t I just throw old electronics in the regular trash?
Electronics contain toxic materials like lead, mercury, and cadmium that can leak into soil and water from landfills. Throwing them in the trash pollutes the environment and poses serious risks to human and animal health.
What does it mean to repair or refurbish a device?
Repairing means fixing a broken device to make it functional again. Refurbishing involves restoring a used device to like-new condition, which often includes cleaning it, replacing worn parts, and updating its software before it is resold.
How do I find a certified e-waste recycler near me?
You can often find certified e-waste recyclers by checking your local municipality’s website or searching online directories like Earth911. Many electronics retailers also offer take-back programs for old devices.
Are companies doing anything to reduce e-waste?
Yes, many companies are starting to adopt more sustainable practices. This includes designing products that are easier to repair, using recycled materials, and offering programs where customers can trade in old devices for recycling.







Leave a Comment