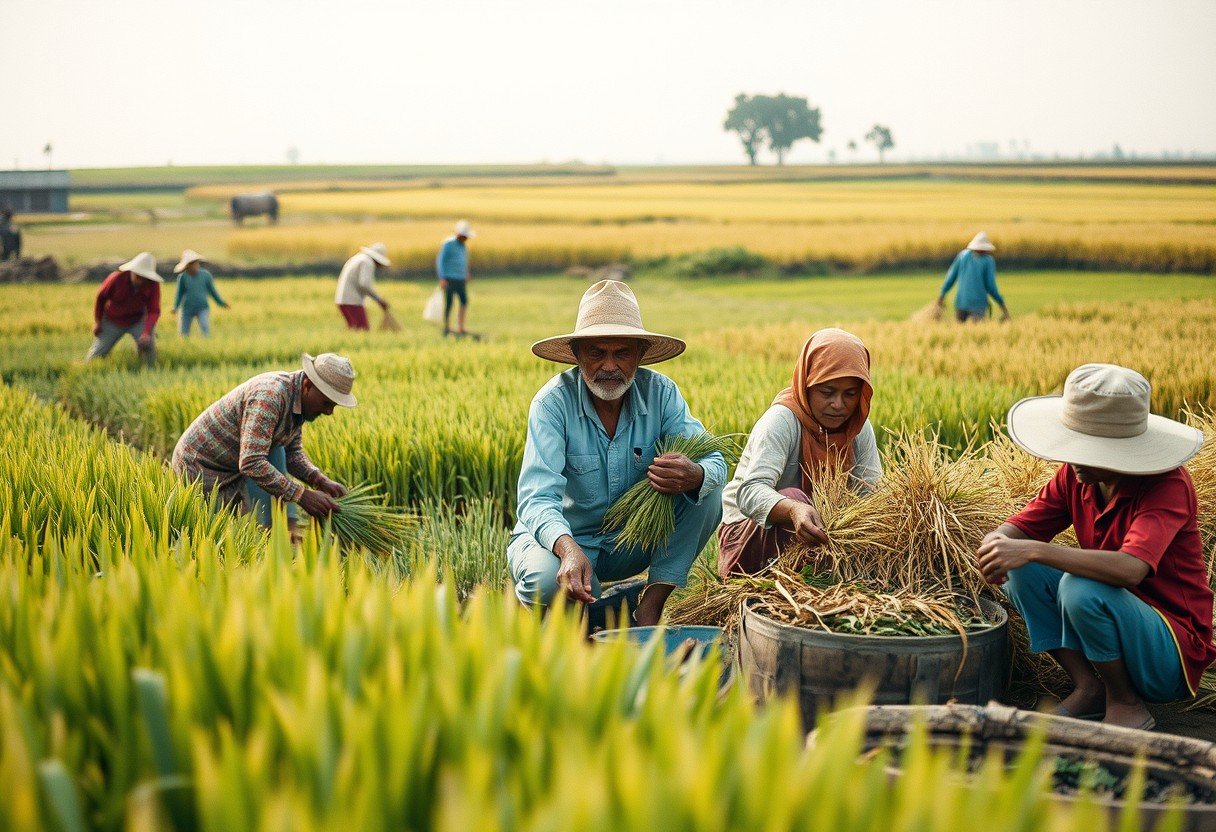
Did you know that the way most people in the world farm is not for selling but for survival? Subsistence agriculture is practiced by the largest percentage of the world’s people, especially in developing countries. This method involves small-scale farmers growing just enough food to feed their own families. This approach is fundamental to the food security and cultural heritage of billions, shaping life in rural communities across Africa, Asia, and Latin America.
Understanding the Two Main Farming Styles
Before diving deep into the most common type of agriculture, it’s helpful to understand the main categories that farming falls into. Globally, agricultural practices can be broadly split into two types: subsistence and commercial. The primary difference between them lies in their goal and scale.
Subsistence farming is all about self-sufficiency. A family grows a variety of crops and raises animals to meet their own needs for food and other essentials. There is very little, if any, surplus to sell at a market.
On the other hand, commercial agriculture is a business. It focuses on producing large quantities of a single crop or type of livestock to sell for profit. This type of farming uses modern technology and is deeply connected to national and international markets.
| Feature | Subsistence Farming | Commercial Agriculture |
| Main Goal | Feed the farmer’s family | Sell crops and livestock for profit |
| Farm Size | Typically small plots of land | Large-scale operations |
| Technology | Uses traditional methods and tools | Relies on modern machinery and tech |
| Output | Diverse crops for family use | Specialized crops for the market |
Why is Subsistence Farming so Widespread?
The dominance of subsistence farming is tied to economic and social conditions in many parts of the world. For billions of people, it is not just a job but a way of life that has been passed down through generations.
This practice ensures a direct source of food, providing a safety net where formal markets are unreliable or inaccessible. Farmers often grow a mix of crops like corn, beans, and potatoes, which helps maintain a varied diet and reduces the risk of total crop failure if one type of plant fails.
It is also deeply integrated with local culture and community. Labor is often shared among family members and neighbors, strengthening social bonds. This reliance on traditional knowledge and local resources makes it a resilient and sustainable option for communities with limited financial capital.
Where in the World is Subsistence Farming Common?
Subsistence farming is the backbone of rural economies in many developing regions. You will find it most prevalent in parts of Africa, Asia, and Latin America, where a significant portion of the population lives in rural areas.
In sub-Saharan Africa, for instance, a vast majority of farmers engage in small-scale farming to survive. Similarly, in countries like India and Bangladesh in South Asia, millions of families cultivate small plots of land to sustain themselves. In the rural highlands of Latin American countries, indigenous communities continue to practice traditional farming methods that have supported them for centuries.
These regions often share characteristics like challenging climates, limited access to modern infrastructure, and economic systems that make commercial farming difficult for the average person to pursue.
Major Challenges for Subsistence Farmers
While it sustains a large portion of the world’s population, subsistence farming is not without its difficulties. Farmers often face a constant struggle against factors that are largely out of their control. These challenges can threaten their livelihoods and food security.
One of the biggest hurdles is the limited access to resources. This includes everything from modern tools and high-quality seeds to financial credit and educational opportunities. Without these resources, it is difficult to improve crop yields or cope with unexpected problems.
Several key issues consistently impact these farmers:
- Climate Change: Unpredictable weather patterns, including droughts and floods, can easily destroy an entire season’s harvest, leaving families with no food or income.
- Inadequate Market Access: Even when farmers have a small surplus, poor roads and lack of transportation often prevent them from reaching markets to sell their goods.
- Soil Degradation: Continuous farming on the same plot of land without modern conservation techniques can deplete the soil of essential nutrients, leading to lower yields over time.
- Lack of Financial Capital: Without access to loans or savings, farmers cannot invest in better equipment, irrigation, or other improvements that could boost their productivity.
How Climate and Economy Shape Farming Practices
No farm exists in a bubble. The choices a farmer makes are heavily influenced by their local climate and the broader economic landscape. Climate dictates which crops can grow successfully, while economic factors determine whether farming is a viable livelihood.
Different climate zones—such as tropical, temperate, or arid—support different types of plants. For example, rice thrives in the wet, tropical climates of Asia, while wheat is better suited to the temperate zones of North America and Europe. Subsistence farmers must use their deep knowledge of local weather patterns to decide when to plant and harvest.
Economic factors like market demand, labor costs, and government policies also play a huge role. Government subsidies can encourage farmers to grow certain crops, while fluctuating market prices can make farming a risky venture. For subsistence farmers, these economic pressures can be particularly intense, as they have little to no financial cushion to fall back on.
The Rise of Technology in Modern Agriculture
While traditional methods remain dominant in subsistence farming, technology is revolutionizing agriculture elsewhere. Innovations are making farming more efficient, productive, and sustainable than ever before.
Practices like precision agriculture use GPS and sensors to give farmers detailed information about their fields. This allows them to apply water and fertilizer only where needed, saving resources and reducing environmental impact. Other modern techniques include hydroponics and vertical farming, which allow crops to be grown indoors without soil.
Biotechnology is also playing a critical role. Scientists are developing genetically modified crops that are resistant to pests, diseases, and drought. These advancements hold the potential to address global food shortages and improve the resilience of our food systems, though access to these technologies remains a major barrier for small-scale farmers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between subsistence and commercial farming?
The primary difference is the goal. Subsistence farming focuses on growing enough food to feed the farmer’s family, while commercial farming is about producing crops and livestock to sell for profit in the market.
Why do so many people still practice subsistence agriculture?
Many people practice it because it provides a direct and reliable food source in regions where economic opportunities are limited and markets are inaccessible. It is also deeply tied to cultural traditions and community life.
What are the most common crops grown by subsistence farmers?
Common crops vary by region but often include staples that are high in calories, such as corn (maize), rice, potatoes, cassava, and beans. Farmers typically grow a variety of crops to ensure food availability throughout the year.
How does climate change affect subsistence farmers?
Subsistence farmers are particularly vulnerable to climate change. Unpredictable rainfall, prolonged droughts, and extreme temperatures can lead to crop failure and food shortages, threatening their survival as they lack the resources to adapt easily.
Can subsistence farmers transition to commercial farming?
Yes, a transition is possible, but it is often very difficult. It requires access to education, financial credit, technology, and stable markets. Many programs by governments and non-profit organizations aim to help farmers make this shift to improve their income and living standards.







Leave a Comment