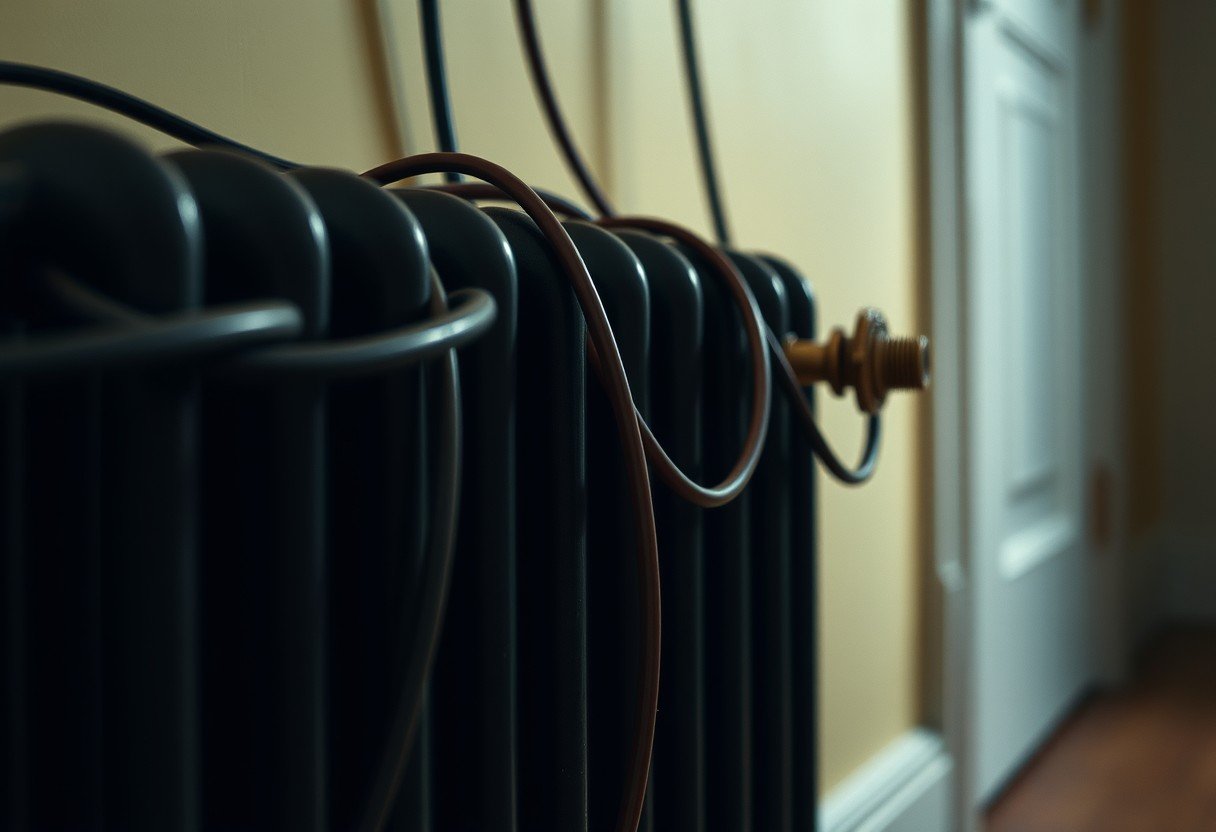
Running cables near a radiator might seem convenient, but it comes with serious risks. The heat from your radiator can damage the wire’s protective insulation over time, potentially leading to electrical failures or even a fire hazard in your home. Understanding how to properly route wiring around heat sources is crucial for ensuring both the safety of your electrical system and your family’s well-being. This guide explains the essential rules and best practices.
Why Running Wires near Radiators is a Concern
The primary job of a radiator is to transfer heat into a room. It does this through both direct contact with the air (conduction and convection) and by emitting infrared energy (radiation). Any object placed too close, including electrical wiring, will absorb this heat.
Over time, this constant exposure to elevated temperatures can cause the plastic or rubber insulation around the wires to become brittle and crack. When insulation fails, the live electrical conductor can become exposed, creating a serious risk of short circuits, electrical shocks, and fire.
Even if the insulation doesn’t fail completely, the heat can increase the electrical resistance in the wire itself, leading to overheating and inefficiency. This puts unnecessary stress on your entire electrical system.
Understanding Different Radiator Types and Heat Output
Not all radiators are created equal. The type you have in your home can influence how much heat it radiates and how close you can safely run wires. From modern panel radiators to classic cast iron models, each has a unique heat emission profile.
Electric radiators, for example, can get very hot on their surface, while baseboard heaters distribute heat along a wider, lower area. Recognizing your radiator type helps you make a more informed decision about safe cable placement. Cast iron radiators retain heat for a long time even after being turned off, meaning any nearby cables are exposed to warmth for extended periods.
Choosing the Right Cables and Insulation
If running wires near a heat source is unavoidable, selecting the right materials is your most important line of defense. Standard household wiring is often not designed to withstand constant high temperatures.
The insulation material surrounding the wire is the most critical component. Different insulators have different temperature ratings, which dictate the maximum heat they can safely endure before breaking down. Silicone and XLPE are known for their excellent heat resistance compared to more common materials like PVC.
Always check the specifications of any cable or wire to ensure it is rated for the environment where it will be installed. Below is a comparison of common insulation types and their typical heat resistance.
| Insulation Type | Heat Resistance |
| PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) | Up to 75°C |
| XLPE (Cross-linked Polyethylene) | Up to 90°C |
| Rubber | Up to 60°C |
| Silicone | Up to 200°C |
| Polypropylene | Up to 70°C |
Key Safety Codes and Regulations to Follow
You don’t have to guess when it comes to electrical safety. Professional electricians follow strict guidelines outlined in the National Electrical Code (NEC) and local building codes. These regulations exist to prevent accidents and ensure all electrical work is performed safely.
While the NEC might not give a single, universal distance for all situations, it provides rules about protecting wires from physical damage and heat. Local codes are often more specific and may dictate a minimum clearance distance for wiring from heating elements like radiators and pipes.
Before starting any wiring project, it is essential to check with your local building authority or consult a licensed electrician. They can provide guidance on the specific requirements in your area, ensuring your installation is both safe and legally compliant.
The Real Dangers: Fire Hazards and Cable Damage
The risks associated with improper wiring near radiators are severe. Degraded insulation is a primary cause of electrical fires in homes. Once the insulation cracks or melts, the live wire can come into contact with other wires or flammable materials like dust, curtains, or wooden baseboards, sparking a fire.
Even without a fire, damaged cables can lead to frequent circuit breaker trips, flickering lights, and damage to sensitive electronic devices plugged into the circuit. These are all signs that your electrical system is under strain and potentially unsafe.
Best Practices for a Safe Cable Installation
To keep your home safe, always follow established best practices when routing wires around radiators and other heat sources. A little bit of planning can prevent major problems down the road.
The most important rule is to maintain a safe distance. While codes vary, a general guideline is to keep standard electrical cables at least 6 to 12 inches away from a radiator’s surface. If this isn’t possible, you must take additional protective measures.
Here are some effective strategies for safe installation:
- Use cables specifically rated for high temperatures, such as those with silicone or XLPE insulation.
- Route wires through a conduit or raceway to provide a physical barrier and an air gap between the cable and the heat source.
- Consider rerouting the cable entirely, even if it means a longer run, to avoid the radiator area completely.
- Regularly inspect any visible wiring near heat sources for signs of discoloration, cracking, or brittleness.
When in doubt, the safest option is always to hire a qualified electrician. They have the knowledge and tools to assess the situation and implement a solution that meets all safety standards.
Common Myths about Wiring near Heat Sources
A common misconception is that modern wires are “heat-proof” and can be placed anywhere. While wire technology has improved, standard PVC-insulated cables are not designed for continuous exposure to the heat produced by a radiator. Assuming they are safe is a dangerous mistake.
Another myth is that as long as the wire isn’t touching the radiator, it’s fine. However, radiators heat the air around them significantly, and this radiant and convective heat can damage insulation from several inches away. A safe air gap is crucial for dissipating heat and protecting the wiring.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the minimum safe distance to run wires from a radiator?
While local codes can vary, a safe general rule is to maintain at least 6-12 inches of clearance between standard electrical cables and a radiator to prevent heat damage to the insulation.
Can I use any type of cable near a radiator?
No, standard cables with PVC or rubber insulation are vulnerable to heat. If you must run a cable near a heat source, you should use one specifically rated for high temperatures, such as those with silicone or XLPE insulation.
What are the signs of heat-damaged cables?
Look for insulation that appears discolored (especially darkened or yellowed), brittle, cracked, or melted. These are clear signs that the cable is too close to a heat source and should be replaced and rerouted by an electrician.
Is it safe to run TV or internet cables near a radiator?
Low-voltage cables like coaxial or ethernet are also susceptible to heat damage. The heat can degrade the protective jacket and potentially affect signal quality over time. It is best to keep these cables away from radiators as well.
What should I do if my existing wires are already too close to a radiator?
You should contact a licensed electrician to inspect the wiring. They can assess for any damage, determine if the cables need to be replaced, and reroute them to a safer location that complies with electrical codes.







Leave a Comment