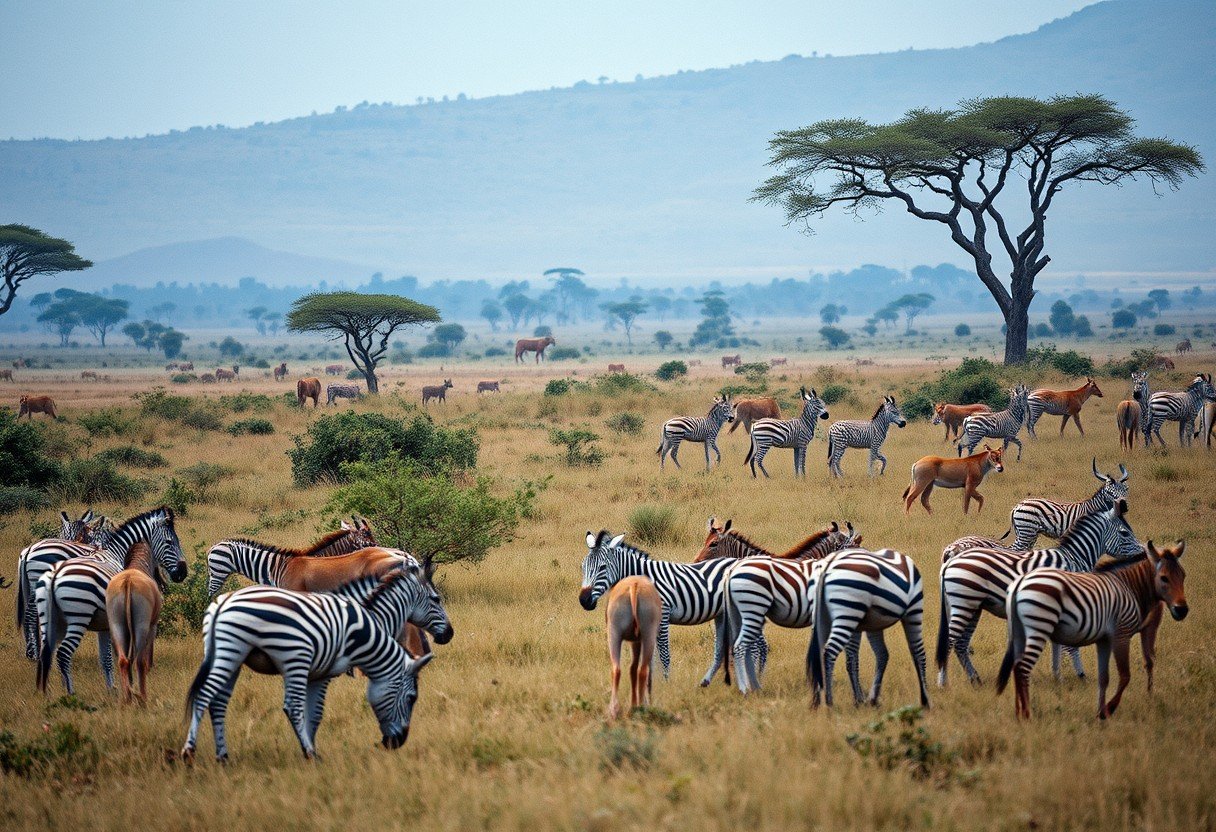
An increase in the herbivore population creates a larger food supply for carnivores, often leading to a rise in their numbers. This predator-prey relationship, however, is part of a complex ecological web. Factors like the environment’s carrying capacity, competition, and habitat health all play a critical role in determining the final outcome for the carnivore population. Understanding this dynamic is key to appreciating the delicate balance of nature.
The Core Relationship between Predators and Prey
Herbivores and carnivores exist in a tightly linked relationship that shapes their entire ecosystem. Herbivores act as primary consumers, transforming plant energy into a food source for other animals. They help manage plant life and spread seeds, which influences the landscape.
Carnivores, in turn, are essential regulators. By preying on herbivores, they prevent overgrazing, which protects plant communities and maintains biodiversity. This natural control allows many different species to coexist and keeps the ecosystem stable. Carnivores often target weak or sick individuals, which fosters healthier and stronger prey populations over time. This process is a fundamental part of how healthy ecosystems function.
Initial Effects of a Growing Herbivore Population
When the number of herbivores increases, the most immediate effect is a greater abundance of food for carnivores. More available prey means predators don’t have to work as hard to find their next meal. This can lead to better health, higher birth rates, and increased survival rates for carnivore offspring.
This initial boom in resources can attract carnivores from surrounding areas, further increasing the local predator population. However, this period of plenty is often temporary. While an increase in herbivores can initially benefit carnivores, the ecosystem has limits that will eventually come into play. The long-term effects depend on how the environment responds to the larger herbivore population.
Why a Carnivore Boom is not Always Guaranteed
Even with more food available, the carnivore population might not grow indefinitely. Several limiting factors can prevent a population explosion and help maintain balance within the ecosystem. The environment’s carrying capacity is a major constraint, as it refers to the maximum population size an area can sustain without degrading the habitat.
Other key factors that can limit carnivore population growth include:
- Habitat Space: Carnivores often require large territories for hunting and raising young. Limited space can lead to conflicts and restrict population growth.
- Disease: As a population becomes denser, diseases can spread more easily, potentially causing a sharp decline in numbers.
- Human Intervention: Activities like hunting, urban development, and habitat destruction can directly limit carnivore populations, regardless of prey availability.
These elements create a natural check on predator numbers, ensuring that they do not grow uncontrollably even when food is abundant.
The Ripple Effect: Overgrazing and Habitat Damage
A significant and prolonged increase in herbivores can lead to serious environmental consequences. With more mouths to feed, herbivores may consume plants faster than they can regrow, a phenomenon known as overgrazing. This can strip landscapes of vegetation, leading to soil erosion and the loss of plant diversity.
This habitat degradation ultimately harms both herbivores and carnivores. As plants disappear, the herbivore population will eventually decline due to starvation. Consequently, if herbivores become scarce, carnivores may also face a decline due to a lack of food. This illustrates how an initial boom can lead to a subsequent bust for both populations.
| Stage | Ecological Event | Impact on Populations |
| Initial Stage | Herbivore numbers increase. | Carnivore population grows due to abundant food. |
| Middle Stage | Overgrazing depletes vegetation. | Herbivore population begins to decline from food scarcity. |
| Final Stage | Herbivore numbers crash. | Carnivore population declines due to lack of prey. |
Increased Competition Among Carnivores
As the carnivore population grows in response to more herbivores, competition for resources can become intense. Even with plenty of prey, predators may still compete for the best hunting grounds, den sites, and mates. This can lead to more aggressive interactions and territorial disputes between individuals or groups.
Some predators may adapt their behavior to cope with the increased competition. For example, they might become more opportunistic, expanding their diet to include other prey, or alter their hunting times to avoid rivals. This behavioral flexibility is crucial for survival in a dynamic environment where the balance of power is constantly shifting.
The Role of Wildlife Management and Conservation
To prevent the boom-and-bust cycle caused by unchecked population growth, wildlife management is often necessary. Conservation strategies focus on maintaining a healthy and balanced ecosystem where both herbivores and carnivores can thrive without causing long-term damage to their habitat.
Effective management not only supports biodiversity but also helps maintain the health of various habitats. This can involve monitoring animal populations, managing land to provide adequate food and shelter, and creating wildlife corridors to allow animals to move safely between different areas. By taking a proactive approach, conservationists can help ensure the long-term stability of predator-prey dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main reason a carnivore population increases when herbivores do?
The primary reason is an increase in food availability. More herbivores mean more prey for carnivores, which supports higher survival and reproduction rates, allowing the carnivore population to grow.
Can too many herbivores actually harm carnivores in the long run?
Yes, an overabundance of herbivores can lead to overgrazing and habitat destruction. This depletes the herbivores’ food source, causing their population to crash, which in turn leads to a food shortage and a decline in the carnivore population.
What is carrying capacity and how does it affect predators?
Carrying capacity is the maximum number of a species that an environment can sustain over time. For predators, it is limited by factors like prey availability, territory space, and water, which prevent their population from growing infinitely.
How do predators help keep an ecosystem healthy?
Predators help control herbivore populations, which prevents overgrazing and protects plant life. They also tend to prey on weaker or sick animals, which helps keep prey populations healthy and genetically strong.







Leave a Comment