From the misty plains of England to the bustling heart of the Aztec empire and the sun-drenched cliffs of New Mexico, ancient civilizations built incredible structures. These monuments, like Stonehenge, the Templo Mayor, and the Sun Dagger, were not just buildings. They were sophisticated tools designed to connect humanity with the cosmos, marking time and celebrating celestial events. They show us how ancient people used astronomy to shape their cultures, rituals, and daily lives across the globe.
A Shared Blueprint Across Continents
It’s fascinating to think that societies separated by thousands of miles and years developed a similar focus. They all looked to the sky and decided to build massive structures that aligned with the sun, moon, and stars.
This wasn’t a coincidence. It shows a universal human need to understand the world and find our place within it. These monuments were the intersection of science, religion, and community life for ancient people. By tracking celestial events like solstices and equinoxes, they could predict seasonal changes, which was crucial for farming and survival.
The architectural skills needed to create these alignments were incredible for their time, demonstrating advanced knowledge of engineering and astronomy that continues to impress researchers today.
Stonehenge: England’s Prehistoric Solar Clock
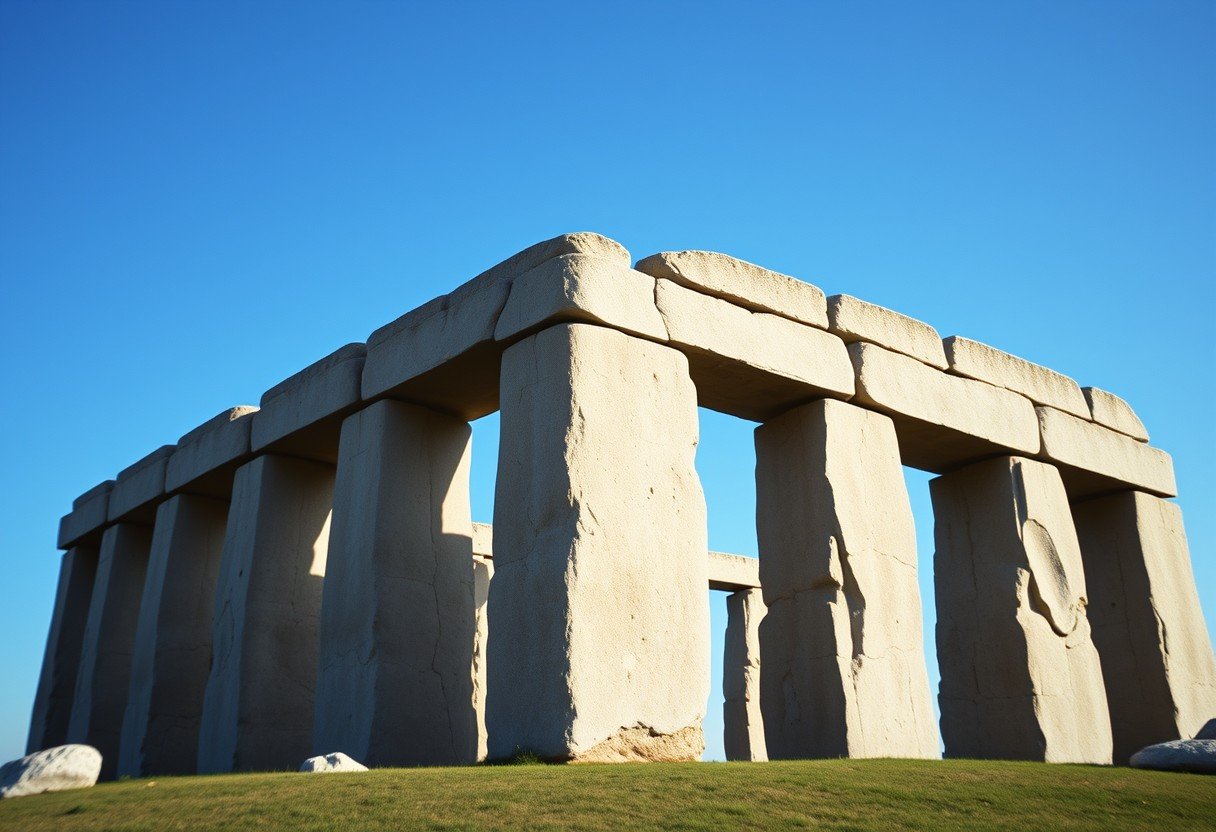
Standing on the Salisbury Plain in England, Stonehenge is perhaps the world’s most famous prehistoric monument. Built around 3000 BCE, its giant stones were hauled from miles away and arranged in a precise circular pattern. For centuries, its purpose was a mystery.
Modern research has confirmed that Stonehenge is a masterclass in ancient astronomy. Its most famous alignment is with the sunrise on the summer solstice, the longest day of the year. On this day, the sun rises directly over the Heel Stone, casting a perfect beam of light into the center of the circle. This suggests it was used as a calendar and for important seasonal rituals.
The monument also has alignments with the winter solstice sunset, making it a year-round observatory that connected its builders to the cosmic cycles.
Templo Mayor: The Aztec Cosmic Center
In the center of the former Aztec capital, Tenochtitlan, stood the Templo Mayor. This massive step-pyramid was the religious and social heart of the empire. It wasn’t just one temple but a dual structure dedicated to two important gods: Huitzilopochtli, the god of sun and war, and Tlaloc, the god of rain and agriculture.
This dual design was intentional and deeply symbolic. During the spring equinox, the sun would rise directly between the two temples. This celestial event marked the beginning of the crop-planting season and the time for warfare, perfectly linking the two deities and their domains. The Templo Mayor was a physical representation of the Aztec cosmos, or their understanding of the universe.
The structure served as a powerful symbol of imperial power and religious devotion, where important ceremonies, including human sacrifices, were held to keep the cosmos in balance.
The Sun Dagger: A Natural Celestial Calendar
Unlike the massive constructions of Stonehenge and the Templo Mayor, the Sun Dagger in New Mexico is a more subtle marvel. Located on Fajada Butte, this sacred site was created by the Ancestral Puebloans. They used three large, naturally fallen rock slabs and carved two spiral petroglyphs behind them.
The genius of the Sun Dagger is how it uses light and shadow.
- On the summer solstice, a single sliver of sunlight, a “dagger,” pierces the exact center of the larger spiral.
- During the winter solstice, two daggers of light appear and frame the same spiral perfectly.
- At the spring and fall equinoxes, a dagger of light cuts through the smaller spiral.
This simple yet precise system served as an accurate calendar. It helped the Pueblo people track seasons for agriculture and schedule important ceremonies. The Sun Dagger shows a deep, harmonious relationship with the natural environment, using the landscape itself as an observatory.
More than just Stones: The Cultural Heartbeat of Ancient Societies
While their astronomical functions are impressive, these sites were much more than calendars. They were the cultural and spiritual centers of their communities, reinforcing social bonds and shared beliefs.
Rituals performed at these locations were essential for maintaining societal order and connecting people to the divine. These architectural wonders served as powerful unifying forces, bringing people together for shared experiences. From solstice celebrations at Stonehenge to sacrificial rites at Templo Mayor, these events reaffirmed cultural identity and passed traditions down through generations.
What These Ancient Wonders Teach us Today
Studying Stonehenge, the Templo Mayor, and the Sun Dagger requires a team effort from different fields. Archaeologists uncover physical evidence, while anthropologists help us understand the cultural context. Modern astronomers can model the sky to confirm the celestial alignments with incredible accuracy.
This interdisciplinary approach gives us a richer picture of the past. It reveals the technological skill and intellectual curiosity of ancient civilizations. These structures are a timeless reminder of our ancestors’ deep connection to the cosmos and their quest to understand their place in the universe.
| Structure | Location | Primary Function | Key Celestial Event |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stonehenge | England | Ritual site and observatory | Summer Solstice Sunrise |
| Templo Mayor | Mexico | Religious and sacrificial center | Spring Equinox Sunrise |
| Sun Dagger | New Mexico, USA | Solar calendar | Solstices and Equinoxes |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main thing Stonehenge, Templo Mayor, and the Sun Dagger have in common?
The most significant similarity is their precise alignment with astronomical events, such as solstices and equinoxes. All three were used to track celestial cycles, serving as calendars and centers for cultural and religious rituals tied to these events.
How did ancient people build structures aligned with the sun?
Ancient builders used meticulous observation, complex calculations, and advanced engineering for their time. They tracked the sun’s path throughout the year to find key positions, like its rising point on the solstice, and then oriented their constructions to match these alignments perfectly.
Why were solstices and equinoxes so important to ancient cultures?
These events marked critical turning points in the year, signaling changes in seasons. This was vital for agricultural societies to know when to plant and harvest crops. They also held deep spiritual meaning, often representing themes of birth, death, and renewal.
Was the Sun Dagger built like Stonehenge?
No, their construction methods were very different. Stonehenge was built by transporting and erecting massive stones, a major feat of engineering. The Sun Dagger is a work of landscape art, using natural rock formations and carved symbols, which shows a different but equally clever approach to creating a celestial observatory.
What kinds of rituals happened at the Templo Mayor?
The Templo Mayor was the center of Aztec religious life, hosting large public ceremonies. These included festivals dedicated to the gods, offerings of food and precious items, and human sacrifices, which the Aztecs believed were necessary to nourish the gods and maintain cosmic balance.







Leave a Comment